-
In July 2020, the US Department of Energy made public its strategy to develop a quantum internet
-
The key resource to make distributed quantum computing possible is entanglement
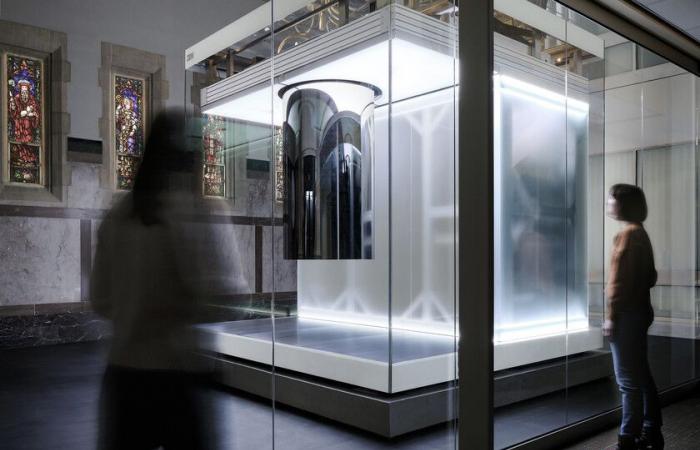
Quantum technologies go beyond quantum computers. We talk a lot about them because during the last five years they have experienced spectacular development, but there is life beyond these very complex machines. Also a quantum internet is being created. In fact, this large-scale quantum communications infrastructure is already underway. In July 2020, the DOE (United States Department of Energy) made public its strategy to promote the development of the technologies that are necessary to deploy a quantum internet.
And hand in hand with this announcement also came the firm commitment to initially invest 625 million dollars in this project. China and the United States are the two great powers that are dedicating the most resources to the development of quantum communications, but Europe is also contributing to this discipline with very significant advances. Deploying a quantum communications infrastructure with global coverage and a reach comparable to that of the Internet network we currently use will allow us to transfer large volumes of information in an essentially instantaneous manner.
Furthermore, data transmission will be carried out in an inherently secure manner because the intertwining between the nodes involved in the communication is broken if it is compromised in any way. Even if someone is simply watching it. Both promises sound great, but we would be wise to temper our likely initial enthusiasm for one compelling reason: the quantum internet is not intended to replace the internet we currently use.
The quantum internet is coming
When it arrives, and we have good reason to predict that it will arrive, it will coexist with the Internet with which we are all familiar in the same way that quantum computers are called to coexist in perfect harmony with classical supercomputers. This reflection invites us to ask ourselves in what applications it makes sense to resort to a quantum conception of the Internet, and the answer emerges by itself from the two properties of this network that we have just investigated: its ability to transfer large volumes of data in a instantaneousness and the inherent invulnerability of quantum communications.
“The key resource to make distributed quantum computing possible is entanglement […] “Distributing it is crucial in all use cases of a quantum network.”
Stephanie Simmons is a physicist, former researcher at Harvard University and co-founder of the quantum communications company Photonic. She recently participated in an event organized by ‘Economist Impact’ and left us several statements that can help us better understand what is the potential of the quantum internet. His company is committed to manufacturing silicon spin qubits interconnected through photonic links because this strategy favors the implementation of a modular and scalable architecture.
“The key resource to make distributed quantum computing possible is entanglement […] Distributing it is crucial in all use cases of a quantum network […] If we manage to distribute the entanglement correctly, we will be able to execute algorithms at scale more quickly,” says Simmons. Another important point that this expert offers us is that the implementation of a distributed system of qubits connected by photonic links allows any two qubits to be entangled. Of course, as long as there is a photonic connection between them because it is essential to carry out the entanglement.
This phenomenon has no equivalent in classical physics, and consists of the state of the quantum systems involved, which may be two or more, being the same. This means that these objects are actually part of the same system, even if they are physically separated. In fact, distance does not matter. If two particles, objects or systems are entangled through this quantum phenomenon, when we measure the physical properties of one of them we will be instantly conditioning the physical properties of the other system with which it is entangled. Even if it is on the other side of the universe.
Everything we have seen so far in this article invites us to foresee that quantum computers connected by photonic links will presumably shape a quantum internet that will have capabilities unattainable by the network with which we are all currently familiar. In fact, if this infrastructure finally prospers and is implemented correctly, scalability will no longer be a problem. And it will be possible to interconnect so many qubits that in a certain way the quantum internet itself will behave like a gigantic quantum computer equipped with millions of qubits. I hope these ideas come to fruition. Cross our fingers.
Image | IBM
More information | The Quantum Insider
In Xataka | MIT holds the key to fully functional quantum computers. And it promises a lot