Samples of quartz They support the idea kite fragmented crashed into the atmosphere of the Land 12,800 years ago, causing a climate change widespread.
Among other things, according to the scientific investigationthat event led to the abrupt reversal of the warming trend of the Land already an anomalous almost glacial period called the Younger Dryas.
UC Santa Barbara Professor Emeritus James Kennett and colleagues report the presence of tracers associated with the cosmic airburst distributed across several separate sites in the eastern United States (New Jersey, Maryland, and South Carolina), indicative materials of the force and the temperature involved in such an event, including platinum, microspheres, molten glass, and shock-fractured quartz.
He study appears in the journal Airbursts and Cratering of ScienceOpen, where details of the discovery.
“What we have discovered is that the pressures and temperatures were not characteristic of the large impacts that form craters, but were consistent with so-called aerial ‘landing’ explosions that do not form many craters,” Kennett said in a statement, regarding the scientific discovery.
The Earth is bombarded every day by tons of celestial debris, in the form of tiny dust particles. At the other end of the scale are the impacts extremely rare and cataclysmic events such as the Chicxulub event that 65 million years ago caused the extinction of the dinosaurs and others species. Its 150 kilometer wide impact crater can be found on the Yucatan Peninsula in Mexico.
Somewhere in between are the impacts that do not leave craters on the Earth’s surface but are nevertheless destructive. The shock wave from the 1908 Tunguska event leveled 2,150 square kilometers of forest, when the asteroid, approximately 40 meters in diameter, struck crashed with the atmosphere almost 10 kilometers above the Siberian taiga.
The comet believed to be responsible for the Younger Dryas cooling episode is estimated to have been 100 kilometers wide, much larger than the Tunguska object, and fragmented into thousands of pieces. The layer of sediment associated with the airburst extends across much of the Northern Hemisphere, but can also be found in places south of the equator. This layer contains unusually high levels of rare materials associated with cosmic impacts, such as iridium and platinum, and materials formed under high pressures and temperaturessuch as magnetic microspheres (cooled metal droplets), fused glass and nanodiamonds.
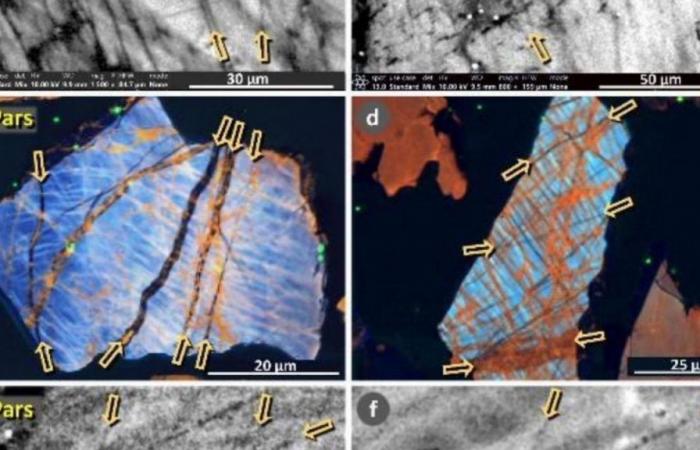
The researchers They are particularly interested in the presence of quartz shocked, indicated by a pattern of lines, called laminae, that show a stress great enough to deform the crystal structure of quartz, a very hard material. This “crème de la crème” of evidence of cosmic impact It is present in impact craters, however, linking shocked quartz to cosmic air bursts has proven to be more challenging.
“In the extreme form, as when a asteroid hits the surface of the Land“If you think about it, the pressures and temperatures that produce these fractures will vary. depending on density, entry angle, impact altitude and impactor size.
“What we have discovered -and this is what is characteristic of the impact layer, called the Younger Dryas Boundary- is that, although we occasionally see examples of ‘traditional’ shocked quartz with parallel fractures in the quartz grains, we mostly see grains that are not parallel.” , said.
These fractures are seen in an irregular, web-like pattern of intersecting and meandering lines and surface and subsurface fissures, in contrast to the parallel, planar deformations of impact-associated shocked quartz found in craters. These subparallel and subplanar deformations are largely due to the relatively lower pressures caused by explosions that occur above the ground, the researchers say, as opposed to impacts that make contact with the ground. Land.
Video: how climate change impacts
Dpa, Airbursts and Cratering from ScienceOpen, Youtube.