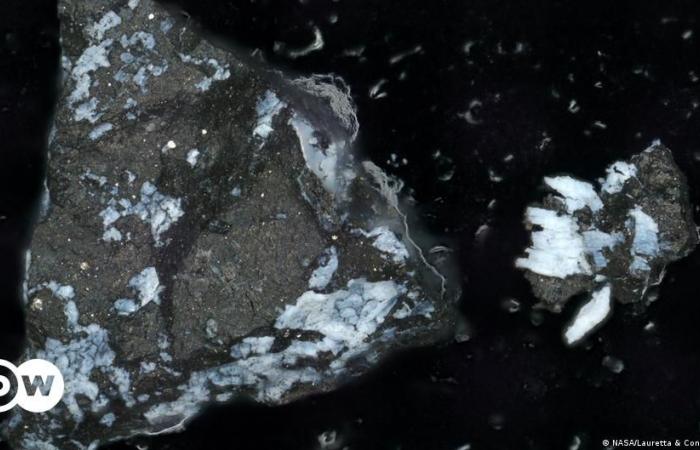
With the aim of studying and learning more about the formation and history of our solar system, on September 24, 2023, NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission successfully brought samples of the asteroid Bennu to Earth.
After analyzing the 121.6 grams of the space rock, NASA scientists have discovered that they contain sodium and magnesium phosphate, indications that it could have originated on an oceanic world, according to a study published this Wednesday (06/26/2024). ) by the journal Meteoritics & Planetary Science.
“These findings underscore the importance of collecting and studying material from asteroids like Bennu,” says a NASA statement. Dante Lauretta, co-author of the paper and principal investigator of OSIRIS-REx at the University of Arizona.
Important components for life
According to astronomers, the asteroid Bennu, which is relatively close to Earth, could provide several clues about the formation of the solar system, since it would have existed when our cosmic neighborhood was forming.
And they were right: the researchers were able to identify carbon, nitrogen, organic compounds and other components essential for life in the samples from Bennu.
“This material holds the key to unraveling the intricate processes of formation of the solar system and the prebiotic chemistry that may have contributed to the emergence of life on Earth,” the expert added.
The surprise of having found phosphate
And to the researchers’ surprise, the asteroid’s dust also contained sodium magnesium phosphate, suggesting Bennu may have been broken off from a small, primitive ocean world that long ago disappeared.
“OSIRIS-REx has given us exactly what we expected: a large, pristine nitrogen- and carbon-rich asteroid sample from a formerly wet world,” said Jason Dworkin, a co-author on the paper.
“The presence and state of phosphates, along with other elements and compounds in Bennu, suggest a watery past for the asteroid. Bennu could have been part of a wetter world. Although this hypothesis requires more research,” adds Lauretta.
Other aspects of interest
In 2020, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) Hayabusa2 mission brought samples from the asteroid Ryugu to Earth. Although phosphates were found on that occasion, the magnesium and sodium phosphate found now stands out for its purity and the size of its grains.
Furthermore, the predominant component of asteroid Bennu is magnesium-containing phyllosilicates, primarily serpentine and smectite, rock types typically found on Earth’s mid-ocean ridges.
“The data we have presented here are just the tip of the iceberg: there is likely more to the sample that we do not know,” the researchers conclude.
Edited by José Urrejola, with information from NASA, Space.com and Meteoritics & Planetary Science.