06/27/2024
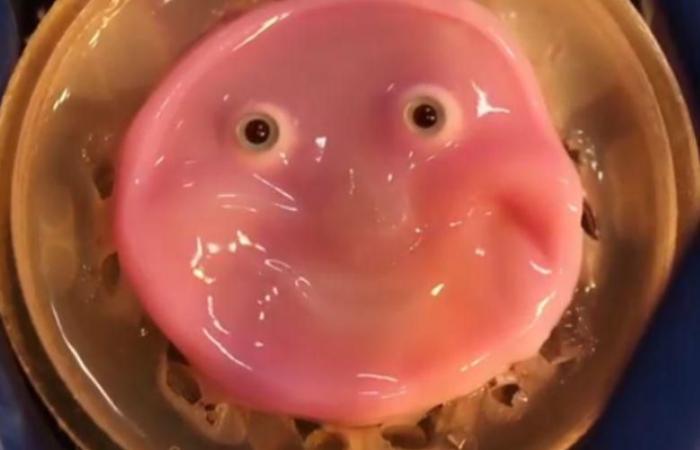
Japanese scientists used human cells for create something equivalent to living skin, which they applied to a robot to make it smile in a realistic, albeit creepy, way.
Researchers at the University of Tokyo published their findings this week along with a video of the pink material that stretches for what is intended to be a smile.
You may be interested: Dating application launched to boost the birth rate in Tokyo
“This pink, fleshy, smiling face is made from living human skin cells and It was created as part of an experiment to allow robots to show emotions.”, explains the international magazine New Scientist.
The developers used a “gel loaded with skin-forming cells” to create a “robot covered in living skin”, according to the study published in the journal Cell Reports Physical Science.
“As the development of AI technology and other advances expand the required roles of robots, the required functions of the robot skin are also beginning to change“,” Michio Kawai of Harvard University explained to the magazine.
The scientist, who participated in the experiment in Tokyo, added that “the ability to recreate the formation of wrinkles on a palm-sized laboratory chip can be used simultaneously to test new cosmetics and skin care products whose objective is to prevent, delay or improve the formation of wrinkles,” he explained about this new development that seeks to replicate human skin.
Also: “We don’t have a red button to turn it off when it gets out of hand”: Martin Hilbert talking about Artificial Intelligence
Although he acknowledged, there are still challenges. “The lack of sensory functions and the absence of blood vessels that provide nutrients and moisture means that can’t survive long in the air (…) To address these problems, “The current challenge is to incorporate neuronal mechanisms and perfusion channels in the skin tissue,” Kawai said according to New Scientist.
According to the organization Physscientific news portal, the experiment led by Professor Shoji Takeuchi would be an alternative to hyper-realistic silicone skin, but scientists want “provide robots with the self-healing capabilities inherent to biological skin,” objective that they are still developing.
cwith information from AFP*