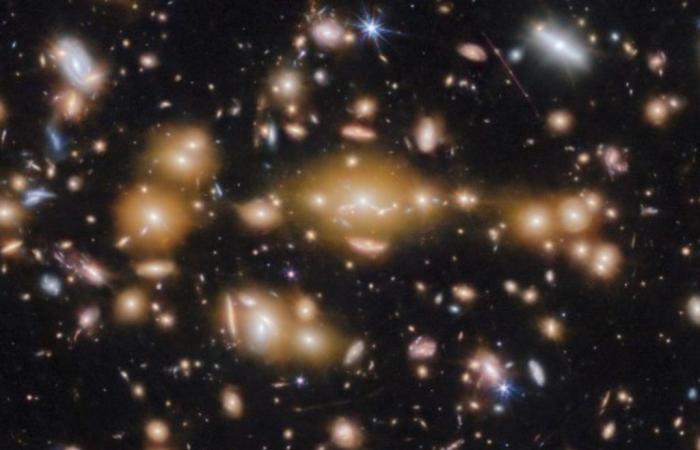
The James Webb Space Telescope continues to surprise, this time conquering a precious loot of “cosmic jewels”: These are five very old star clusters, the first seen in a young galaxy, unless 500 million years have passed since the Big Bang.
Her discovery, useful for reconstructing the evolution of galaxies in the primordial universe, is published in Nature by an international team led by the Italian astronomer Angela Adamo from Stockholm University, in which participants Eros Vanzella and Matteo Messa from the National Institute of Astrophysics of Bologna.
The young galaxies of the primordial universe hold a rich treasure trove of information, because they experienced phases of intense star formation in which large amounts of ionizing radiation were generated, making the universe more transparent (in the so-called era of reionization).
Such distant galaxies are difficult to observe, but fortunately the universe itself offers help through “gravitational lenses”that is, distributions of matter so dense that they curve space-time and deviate the path of light rays, amplifying the light coming from the most distant galaxies.
It is thanks to this effect that a very young galaxy was discovered, called Cosmic Gems Arcwhich we see as it was just 460 million years after the Big Bang.
The stellar jewel loot that James Webb showed off. Photo: X
First observed by the Hubble Space Telescope in 2018, its “heir” James Webb (JWST) is now shown in detail managed by the space agencies of Europe (ESA), the United States (NASA) and Canada (CSA).
The internal properties of a galaxy so far away have never been observed before..
Details of the discovery
In particular, the researchers managed to identify five star clusters, each of which has a size of about 3-4 light years: this indicates that these are very dense clusters, a thousand times larger than the typical young star clusters that can be observed in the local Universe.
“The shock and awe was incredible when we first opened Webb’s images,” said Angela Adamo, originally from Sicily. “We saw a small chain of bright spots, reflected from side to side: These cosmic gems are star clusters! Without Webb we would not have known we were observing star clusters in such a young galaxy,” he added.
The presence of such dense and massive star clusters is relevant for two reasons. Firstly, they could be the precursors of the globular clusters that populate today’s galaxies.
Secondly, these young star clusters, during their formation, can “destroy” the interstellar medium of the host galaxy and, with their young and massive stars, play a key role in the process of reionization of the universe.
“Finally, we are unmasking the origins of the first galaxies with the quality and power of the JWST telescope and, thanks to gravitational lensing, we are seeing unprecedented details,” Vanzella added. “The universe then was not like today’s and now this seems like a fact to us,” she concluded.
James Webb, trend on Google
The James Webb Telescope was trending on Google during the week of June 24. This is demonstrated by the following graph offered by Google Trends.
In turn, the terms “Star” and “Astronomy” also showed peaks of interest throughout the days.