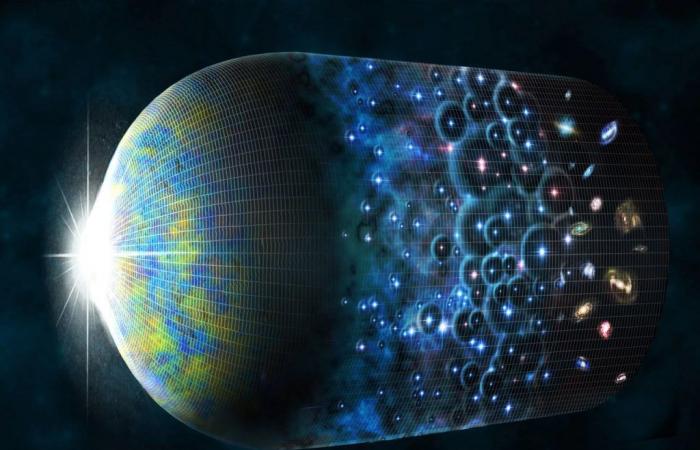
In the beginning of time, there was practically nothing…except for the vastness of the observable universe, with all its matter and radiation compressed into an incredibly dense and hot mass just a few millimeters in diameter.
Yes, it sounds incomprehensible. That’s why Stephen Hawking, The brilliant British physicist, cosmologist and writer has pointed out that nothing that could have existed before the beginning of the universe as we know it has anything to do with what came after… and that there is no theory that can explain it.
For Hawking, at the time of his Origin, the universe was a singularity, an instant in which all the laws of physics would cease to apply. And about 13.8 billion years ago, the cosmos began to experience a rapid expansion that we know as “Big Bang”, a unique cosmic cataclysm.
After that initial expansion, which lasted just a fraction of a second (one trillionth of a second), gravity began to slow down the universe. But space would not stay like this, because 9,000 million years After the Big Bang, its expansion began to accelerate, driven by an unknown force that scientists have called dark energy.
Story of a discovery
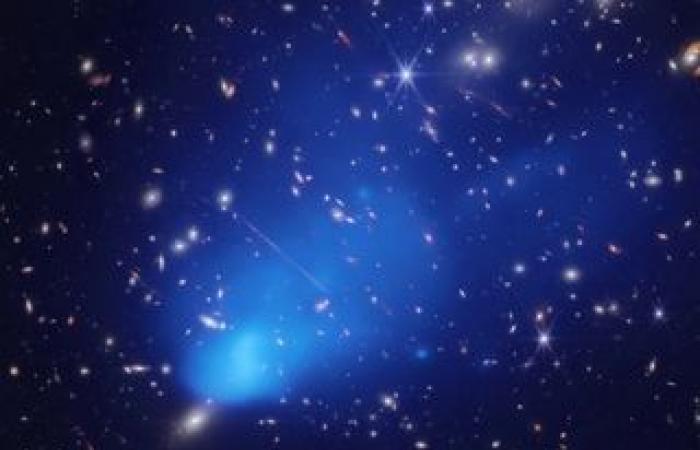
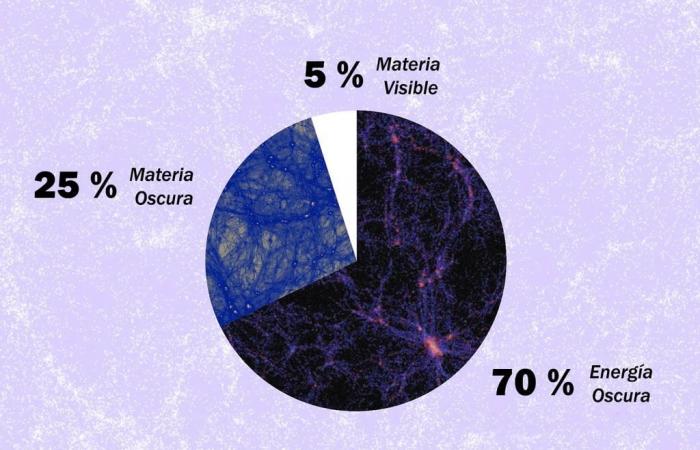
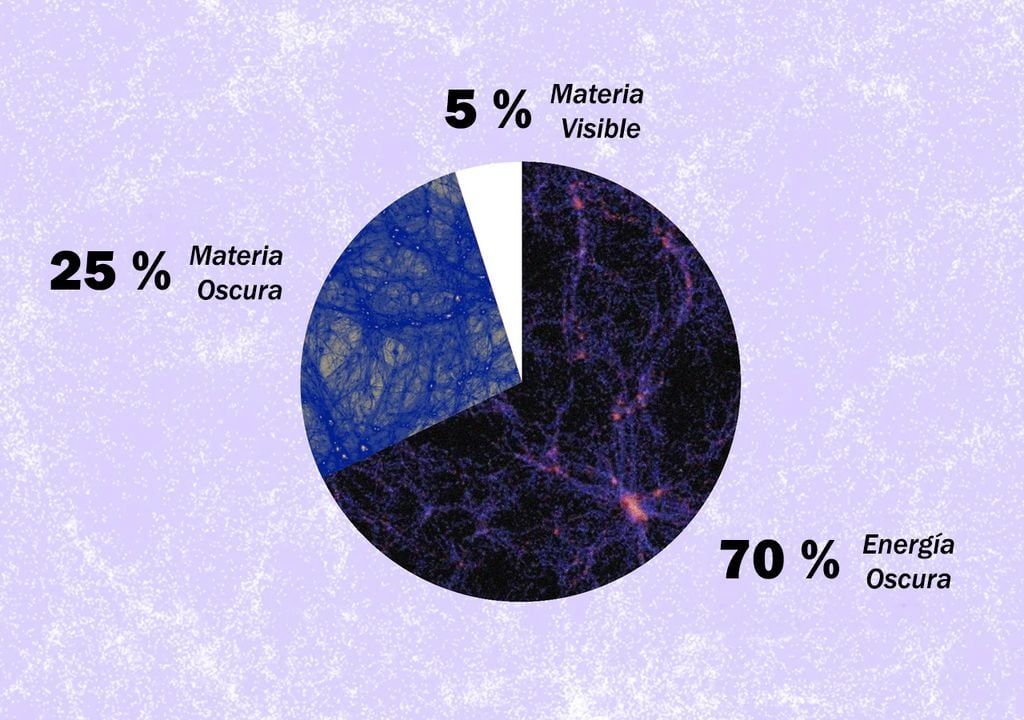
The atoms that make up everything known constitute only 5% of the cosmos. The remaining 95% is what scientists call dark energy. (almost 70%), and 25% is what is known as dark matter. Both carry the adjective “dark” because we do not see them.
In 1912, thanks to the independent work of American astronomers Henrietta Swan Leavitt and Vesto Slipher, It was possible to observe the speed with which the galaxies were moving away from us. These observations were the beginning of many future scientific advances: in 1922, the Russian scientist and mathematician Alexander Friedmann, based on the Albert Einstein’s theory of general relativity published in 1917, proposed that the universe was expanding.
In 1927, the belgian astronomer Georges Lemaître concluded, independently and also taking into account Einstein’s theory of general relativity, that The universe expands, despite the fact that Einstein stated in his theory that the universe was static.
In 1929, the astronomer Edwin Hubble confirmed, using data from the astronomer Milton Humason that the universe is really expandingin what is known today as Hubble’s Law or the Hubble-Lemaître law.

In 1998, two different teams of astronomers who were observing distant supernovae, realized that they had moved away much faster than expected. This could only indicate that the universe itself must be expanding faster as time goes by. This work was awarded with the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2011.
Now all that was left to discover What was driving the universe to expand faster? in the time.
So… what is dark energy?
The short answer is: we do not know. dark energy is just the name astronomers gave to the mysterious “something” that is causing the universe to expand at an accelerated rate. Dark energy was not discovered until the late 1990s.
dark energy It is one of the great mysteries of the universe. For decades, scientists have developed theories about our expanding universe. Now, for the first time, we have tools powerful enough to test these theories and really investigate the big question: “What is dark energy?”
ESA’s Euclid mission (European Space Agency), launched in 2023, will create a 3D map of the universe to observe how matter has been torn apart by dark energy over time. This map will include observations of billions of galaxies that are up to 10 billion light years away from Earth.
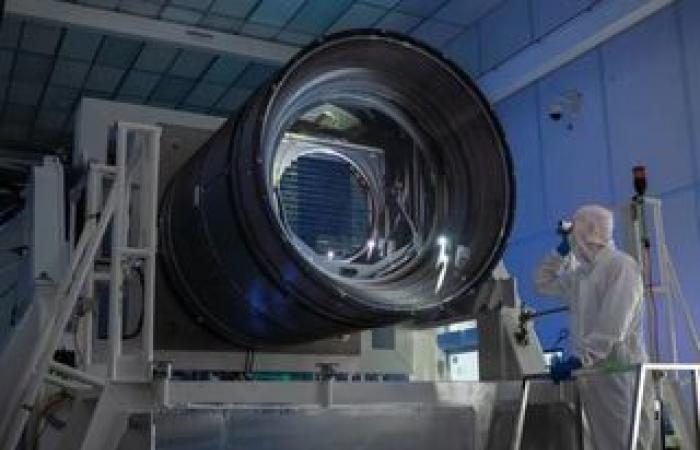
The largest camera built by man reaches its destination: 3200 megapixels to portray the cosmos

NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescopescheduled for release in May 2027, is designed to investigate dark energy and will also create an ultra-high-definition 3D map of dark matter. The Vera C. Rubin Observatory, Currently under construction in Chile and scheduled to open in 2025, it is also set to support our growing understanding of dark energy.
Dark energy is not the same as dark matter
Dark matter is matter that does not interact with the electromagnetic field, so we cannot see it, nor is it absorbed or reflected by the materials. We only know that it exists because, as with dark energy, astrophysics and cosmology have provided many clues to its presence.

The Dark matter is another material component in Einstein’s equations, and is the dominant component of the cosmos: about five times more abundant than ordinary matter (atoms). Forks capable of counteracting the expansion of the universe only up to a certain point.
“Our understanding of reality is not complete, far from it. Reality exists independently of us.” Andrei Linde, Stanford University.
Lastly, although dark energy is not the same as dark matterare similar for a single characteristic: We don’t know what they really are.