In a surprising turn of events, Ethereum gas fees have fallen to their lowest level in years, even though activity on the network is at an all-time high. This phenomenon has become a crucial topic of interest for the crypto community, developers and investors. Below, we will explore in detail the causes and implications of this situation, as well as its impact on the Ethereum ecosystem.
Ethereum Gas Fees: In-Depth Analysis
Gas fees are the costs associated with making transactions on the Ethereum network. These fees are critical to the functioning of the network, as they incentivize miners and validators to process transactions and secure the blockchain. Historically, gas rates have fluctuated considerably due to various factors, such as transaction demand and rate market efficiency.
According to recent Dune Analytics data collected by @hildobby, median gas prices on the Ethereum mainnet fell below 3 gwei for the first time since early 2020. This decline has led to noticeably low dollar rates: a trade on Uniswap costs $1.06, trading an NFT on Seaport costs $1.49, and transferring ETH on-chain costs just $0.23.
Rate market efficiency
Brian Smocovich, founder of Pistachio.fi, explained that the decrease in fees is not the result of a decrease in transaction activity, but rather a more efficient fee market. Smocovich notes that the daily transaction volume on Ethereum is the same or even higher than it was six months ago. The improvement in efficiency is due to the adoption of Layer 2 solutions and the implementation of EIP-4844, which have optimized the Layer 1 rate market.
Layer 2 solutions, like Base, have played a crucial role in reducing gas rates. These solutions allow transactions to be carried out at a significantly lower cost. For example, on Base, a trade on Uniswap costs just $0.0016 in fees, a trade on Seaport costs $0.0021, and an ether transfer costs $0.00026. These figures demonstrate the ability of Layer 2 solutions to ease the load on the core network and reduce transaction fees.
IT MAY INTEREST YOU: Why is the price of bitcoin falling today?
Implications for Ethereum supply dynamics
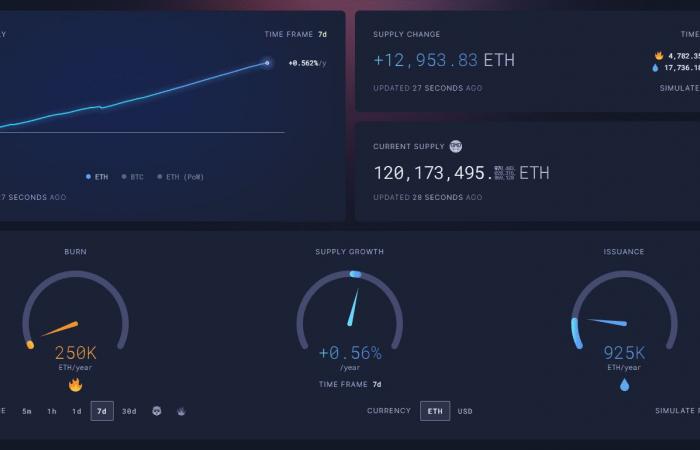
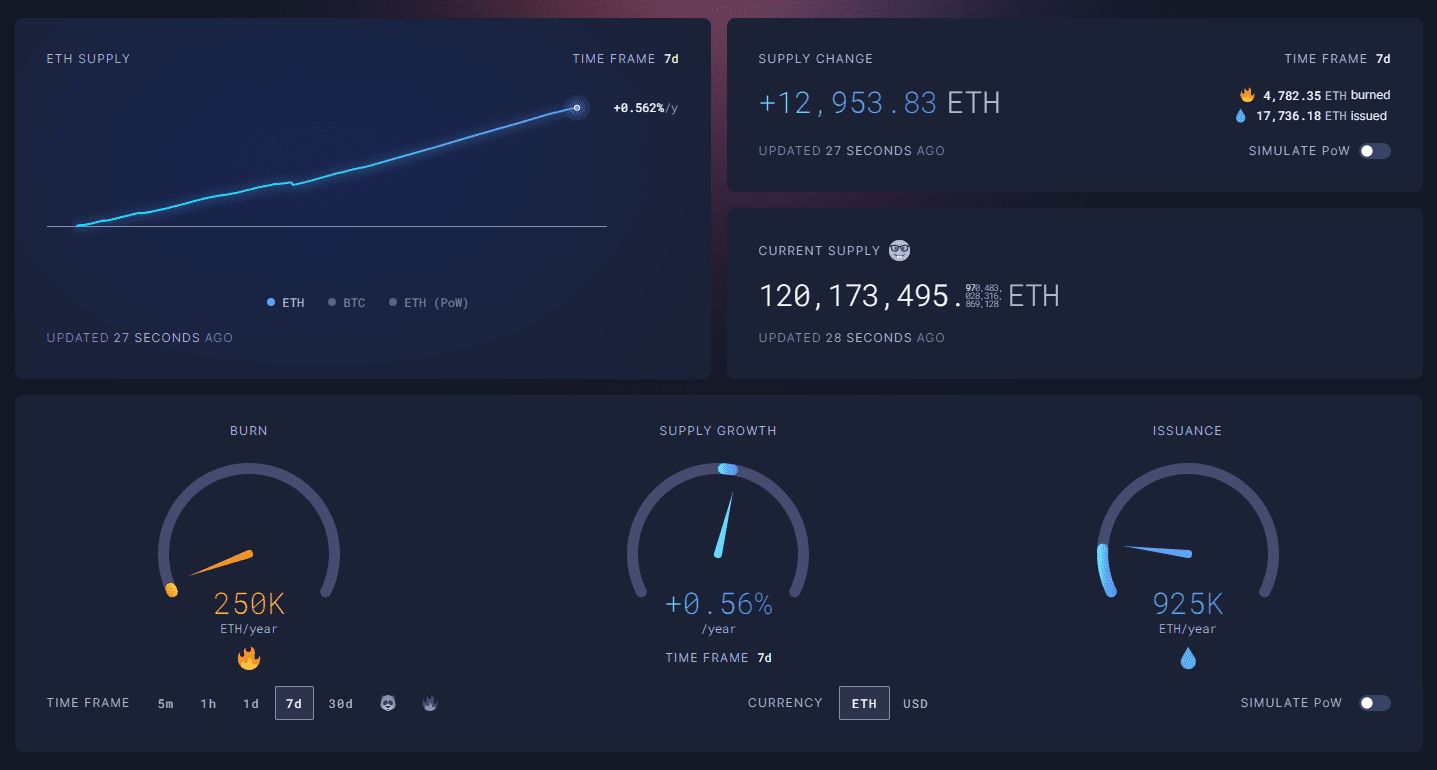
The reduction in gas fees also has major implications for Ethereum supply dynamics. With the introduction of EIP-1559 via the London hard fork, a usage-linked base fee was established that would be burned, thus removing ETH from the total supply. However, with gas fees at such low levels, Ethereum’s burn rate has decreased, leading to slight inflation in the ether supply.
Currently, the ether supply growth rate stands at around 0.56% annually, according to data from ultrasound.money. Although this rate is relatively low, it represents a significant change compared to the period immediately following the implementation of EIP-1559, when tariff burning was contributing to more pronounced deflationary pressure.

Increased activity on the network
Despite the decrease in gas fees, activity on the Ethereum network has reached record levels. According to data from L2Beat, Layer 1 and Layer 2 protocols recorded an average of 299 transactions per second on June 21. This increase in activity is a positive sign for the Ethereum ecosystem as it indicates increasing usage and adoption of the network for various decentralized applications (dApps).
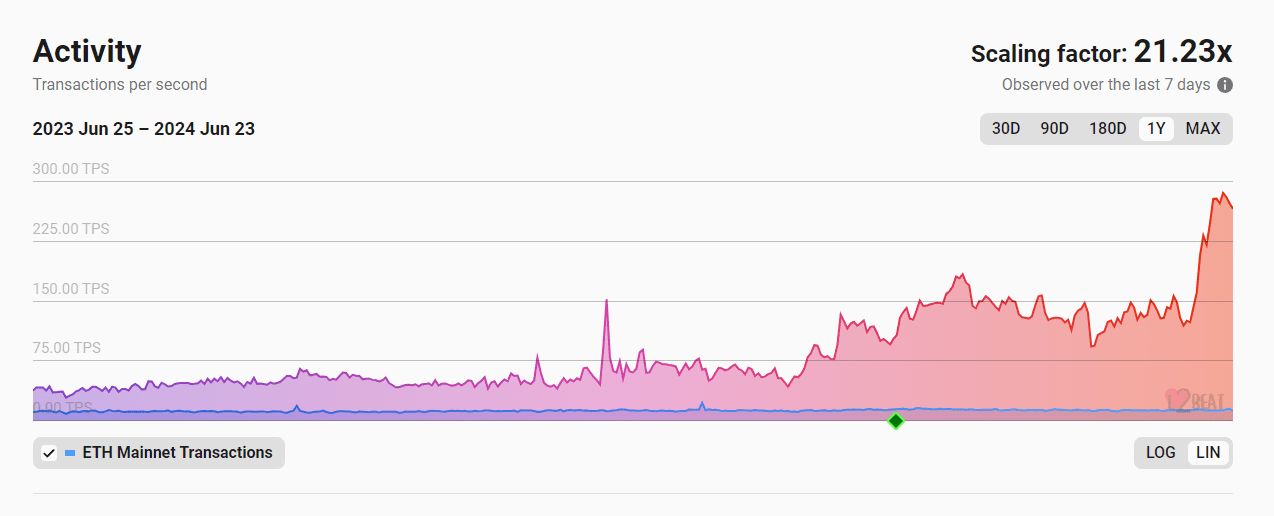

Several factors have contributed to the increase in activity on the Ethereum network. Among them are the growing popularity of decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and other decentralized applications that are attracting users and developers. Additionally, improved network efficiency thanks to Layer 2 solutions has facilitated a greater number of transactions at lower costs.
Benefits for users and developers
Decreasing gas rates and increasing grid activity present several benefits to users and developers. Users can transact at significantly lower costs, encouraging greater participation in the network. For their part, developers can create and deploy decentralized applications without worrying about high gas fees, making it easier to innovate and develop new solutions in the Ethereum ecosystem.